Eng. Roberta Della Gatta
roberta.dellagatta@unina.it
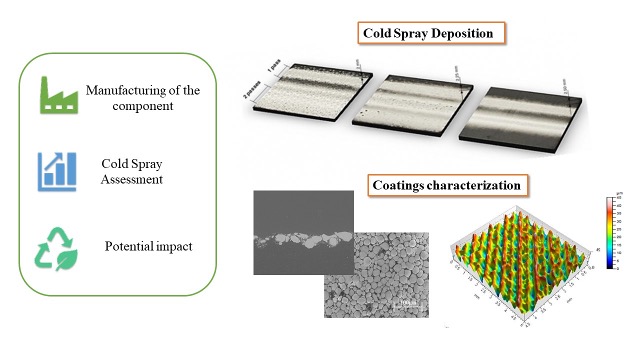
Roberta Della Gatta’s work is focused on the metallization of polymer and fiber-reinforced polymers by means of Cold spray technology, a technique that belongs to the wider family of additive manufacturing. The metallization of the above-mentioned materials is required in order to provide final components that combine the properties of polymers and fibers reinforced polymers, i.e. lightweight and resistance to corrosion, and the properties of the metals, i.e electrical conductivity and thermal protection. To date, this specific application of the Cold Spray technique is at its early stage and a detailed study of the entire manufacturing process is required. For this purpose, the presented doctoral work aims to give a complete knowledge of the Cold Spray process, trying to understand why certain phenomena occur during the process and answer the main unsolved questions about the subject matter. A comprehensive analysis of the entire process is proposed, starting from the manufacturing of the main components, going through the optimization of the cold spray process parameters to the assessment of the potential environmental impacts associated with the materials and energy inputs. The objective is to provide guidelines for the manufacturing of customized polymer/composite components and to identify the best technology suitable for further cold spray application. Likewise, the estimation of the environmental impacts associated with the final products is crucial to compare the Cold spray process to other coating techniques, establishing an inventory of environmental releases.